Advertisement
Google Ad Slot: content-top
Spring boot introduction
Spring Boot is a Java-based framework designed to simplify the development of standalone, production-ready, and microservices-based applications. It is built on top of the Spring Framework and removes the need for extensive configurations, making development faster and more efficient.
Key Features of Spring Boot
Auto-Configuration – Automatically configures Spring components based on project dependencies.
Spring Boot Starters – Predefined dependencies to simplify development.
Embedded Servers – Comes with built-in servers like Tomcat, Jetty, and Undertow.
Production-Ready Monitoring – Includes Spring Boot Actuator for health checks and metrics.
Microservices Support – Ideal for developing RESTful APIs and Microservices.
Externalized Configuration – Supports application.properties and application.yml for easy configuration management.
Spring Boot vs Spring Framework vs Spring MVC
Feature |
Spring Framework |
Spring Boot |
Spring MVC |
|---|---|---|---|
Configuration |
Requires manual setup (XML/Java-based) |
Auto-configured |
Uses Spring Framework |
Boilerplate Code |
High |
Minimal |
Moderate |
Embedded Server |
No |
Yes (Tomcat, Jetty) |
No |
REST API Support |
Requires setup |
Built-in support |
Requires setup |
Microservices |
Not directly supported |
Ideal for Microservices |
Not ideal |
Why Use Spring Boot? (Advantages)
🔹 Reduces Boilerplate Code – No need for extensive configurations.
🔹 Fast Development – Spring Boot starters and auto-configuration save time.
🔹 Microservices Friendly – Easily build distributed applications.
🔹 Standalone Applications – No need for an external server; runs with java -jar.
🔹 Production-Ready – Built-in monitoring and logging.
Spring Boot Architecture
Spring Boot follows a layered architecture consisting of:
🔹 Presentation Layer – Handles user requests (Controller, HTML, JSON).
🔹 Service Layer – Contains business logic and services.
🔹 Repository Layer – Interacts with the database (Spring Data JPA, Hibernate).
🔹 Database Layer – Stores application data.
Spring Boot Auto Configuration
Spring Boot automatically configures components based on dependencies.
Example: If Spring Boot Starter Web is present, it auto-configures Tomcat as an embedded server.
Hello World Example in Spring Boot
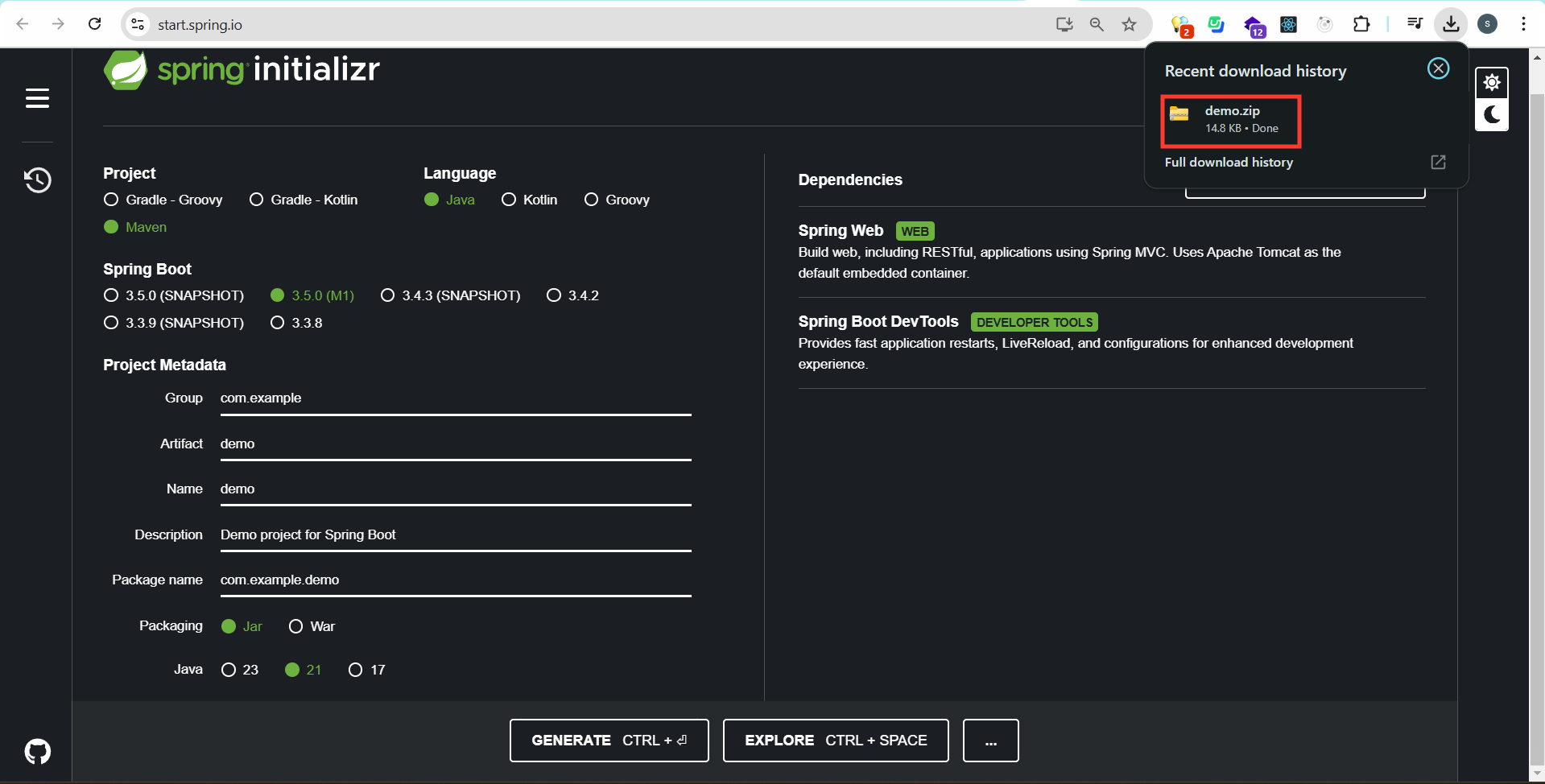
Step 1: Create a Spring Boot Project (Using Spring Initializr)
- Visit Spring Initializr
- Select Maven/Gradle, Java, Spring Boot version
- Add Spring Web, Spring Boot DevTools dependencies
- Click Generate, then extract the downloaded ZIP
Step 2: Create the Main Application Class
Step 3: Create a Simple REST Controller
- Run the application
- Open
http://localhost:8080/api/helloin a browser - Output: Hello, Spring Boot!