Advertisement
Google Ad Slot: content-top
Introduction to Spring Security
Spring Security is a powerful and customizable framework used to secure Java applications. It provides authentication, authorization, and protection against common security threats.
Introduction to Spring Security:
Spring Security is a framework that provides:
- Authentication (Who are you?)
- Authorization (What are you allowed to do?)
- Protection against common security threats like CSRF, XSS, and Session Fixation.
Key Features
Secure endpoints with minimal configuration
Support for various authentication methods (DB, LDAP, OAuth2, JWT)
Method-level security (@PreAuthorize, @PostAuthorize)
Built-in password hashing (BCrypt, PBKDF2)
Adding Spring Security to a Spring Boot Project
Spring Boot simplifies security by auto-configuring it when you add the dependency.
Testing the REST API with Postman:
Once the application is running, test the endpoints:
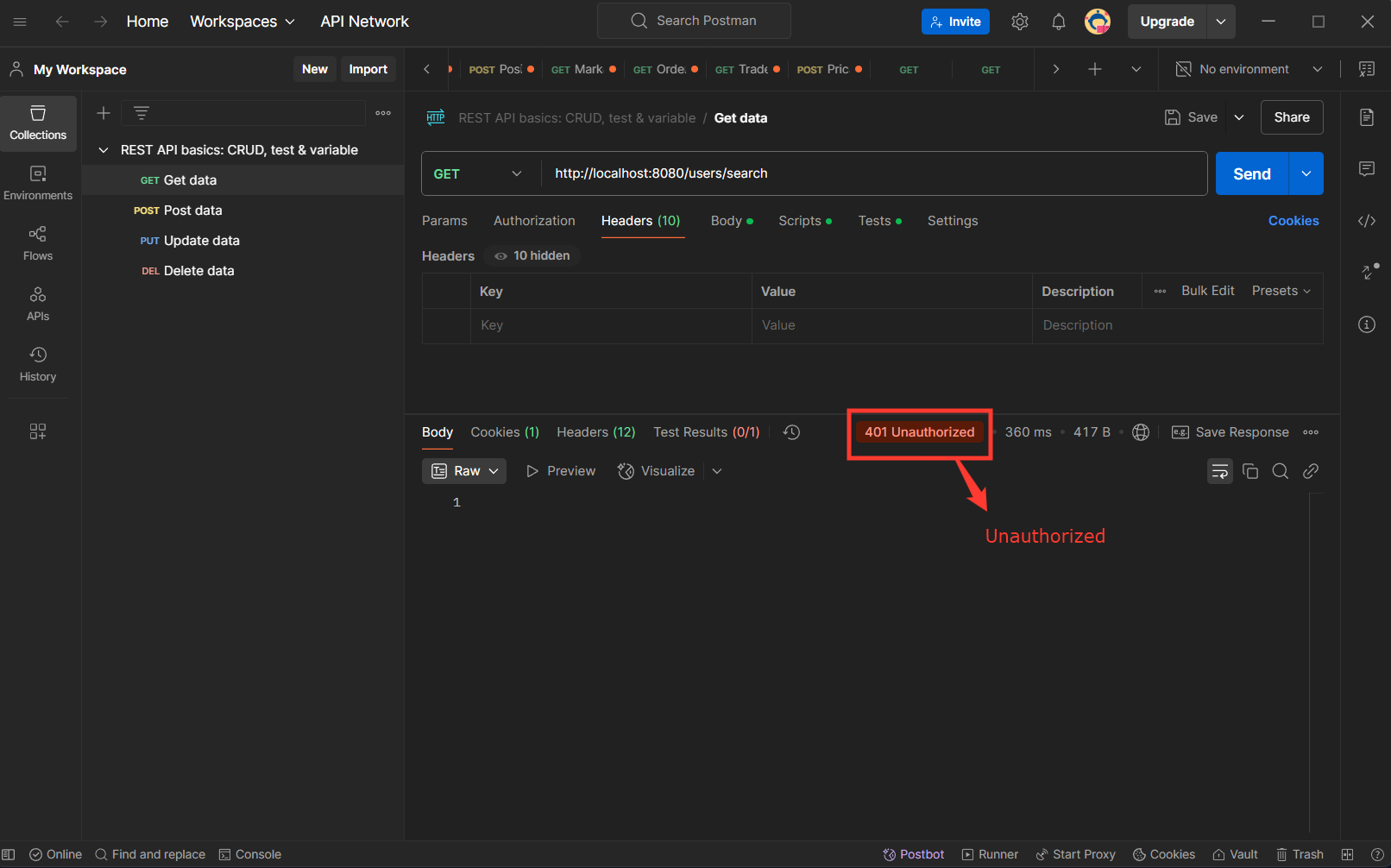
Default Security Behavior in Spring Boot
When you add spring-boot-starter-security, Spring Boot:
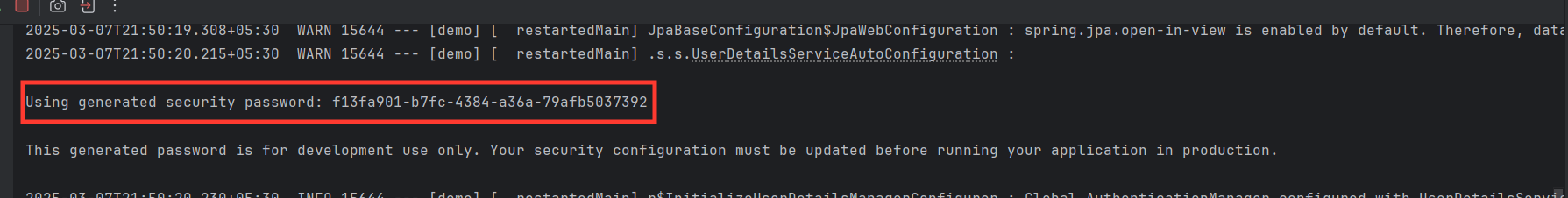
- Enables Basic AuthenticationThe default username is "user", and the password is randomly generated (logged in the console).
- Protects all endpointsIf you try to access any URL without authentication, you’ll get a 401 Unauthorized error.
- Uses Form-based LoginIf you're using a web application, a default login page is provided.
Default Login Credentials Check the generated password in logs:
Testing the REST API with Postman:
Once the application is running, test the endpoints:
Set Basic Auth Username and Password
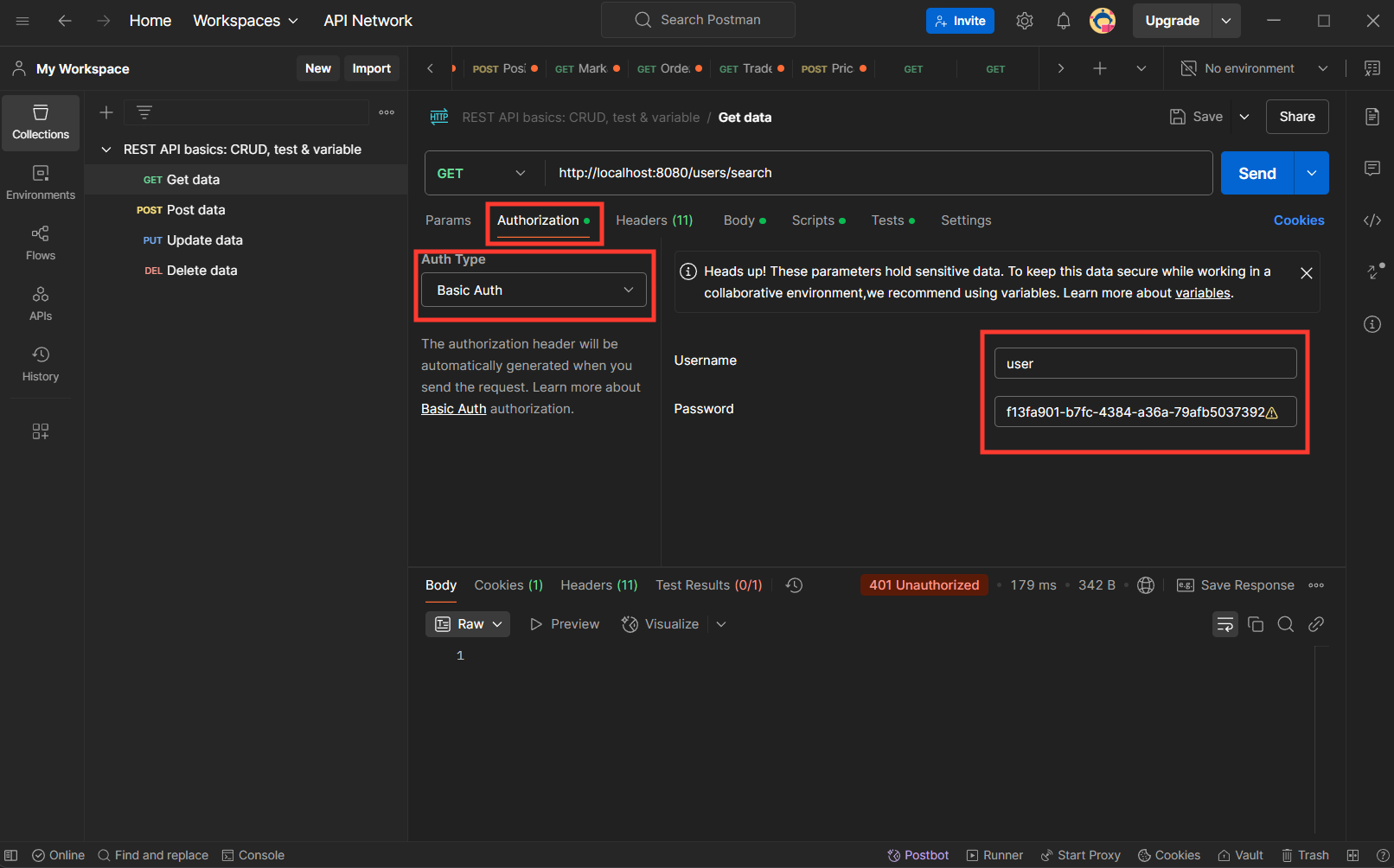
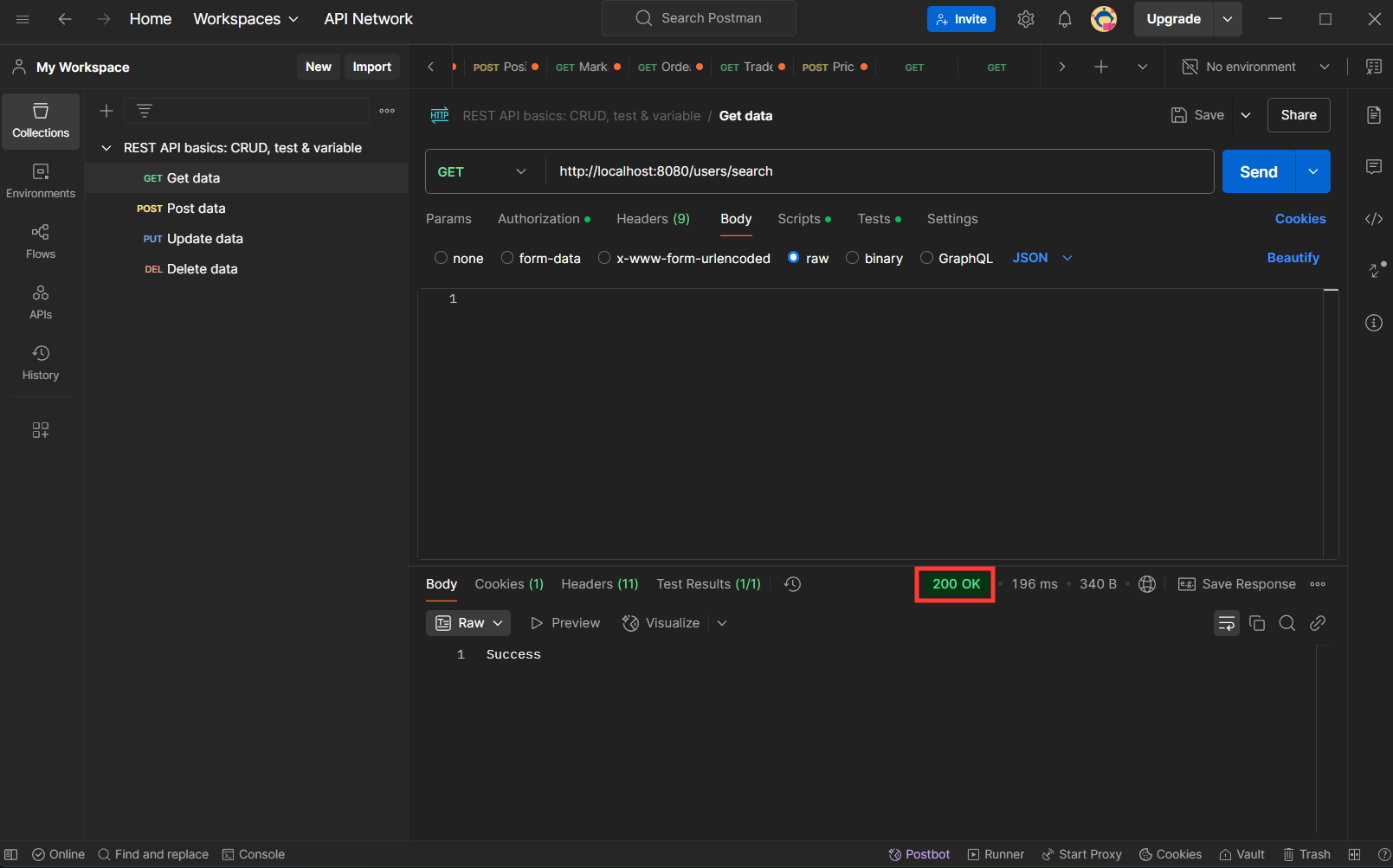
Understanding SecurityAutoConfiguration
Spring Boot auto-configures security through SecurityAutoConfiguration, which:
- Creates a default user
- Enables form login
- Applies a default security filter chain
How does it work? Spring Boot detects spring-boot-starter-security and applies the default security settings.
🔹 To customize security, you must override the default security configuration.
Disabling Default Security Configurations
If you want to disable security (not recommended in production):
🔹 Method 1: Exclude SecurityAutoConfiguration
Add this to your application.properties file:
Or exclude it in the main class:
🔹 Method 2: Define a Custom Security Configuration
A better approach is to override the default security settings using SecurityFilterChain will explain later topics.
✅ This will disable the default security but allows you to implement custom authentication.