Advertisement
Google Ad Slot: content-top
Authentication & Authorization in Spring Security
Authentication and authorization are core concepts in security. Let’s explore them in detail.
- Authentication vs. Authorization
- Custom User Authentication
Authentication vs. Authorization
🔹 Authentication: Confirms "Who are you?" (identity verification)
🔹 Authorization: Determines "What are you allowed to do?"
Example:
- Login with username/password → Authentication
- Checking if user has "ADMIN" role → Authorization
How Spring Security Handles Authentication & Authorization?
- Authentication: Managed via
UserDetailsService,AuthenticationManager - Authorization: Controlled via
SecurityFilterChainor annotations like@PreAuthorize
Custom User Authentication
By default, Spring Security provides an in-memory user. But in real applications, we authenticate users from a database.
Step 1: Create a User Entity
Table name : user
| id | username | password | role |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | John | $2a$12$PypIq6C.MQ4dPia2piWMZO5vZIq2OFqmA4x9YAtm11ndY6VrfdUZy (john@123) | ADMIN |
| 2 | Mike | $2a$12$fv/xTvNU0S9LoQQo2nTPLurmuMSRlYmYP.DPRjLLHbJQjw9RZ4wcq (mike@123) | USER |
Bcrypt password generated here
Step 2: Configure UserRepository
Step 3: Implement UserDetailsService
This tells Spring Security how to fetch user details from the database.
Step 4: Configure Authentication in SecurityConfig
Step 5: Configure USerController
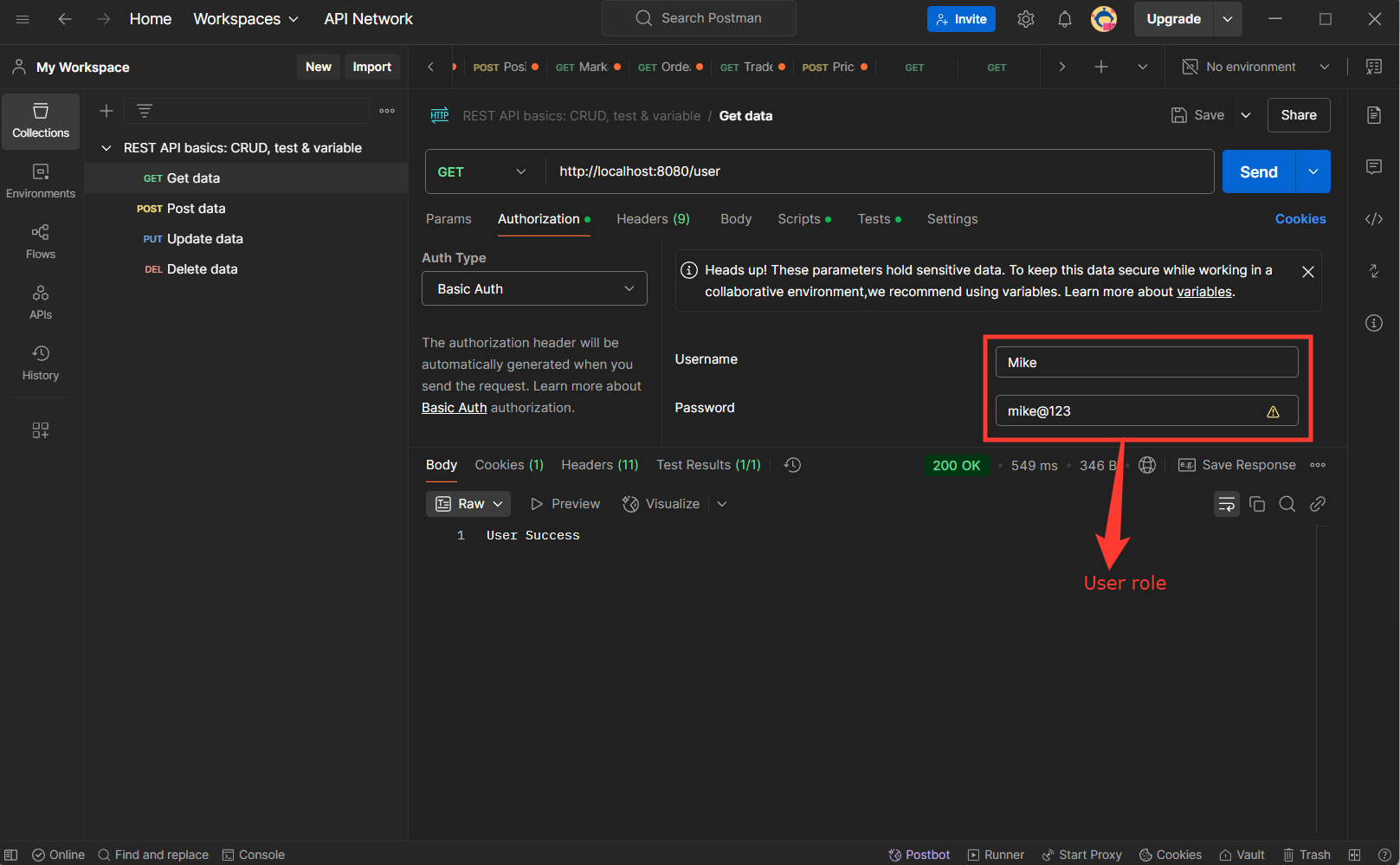
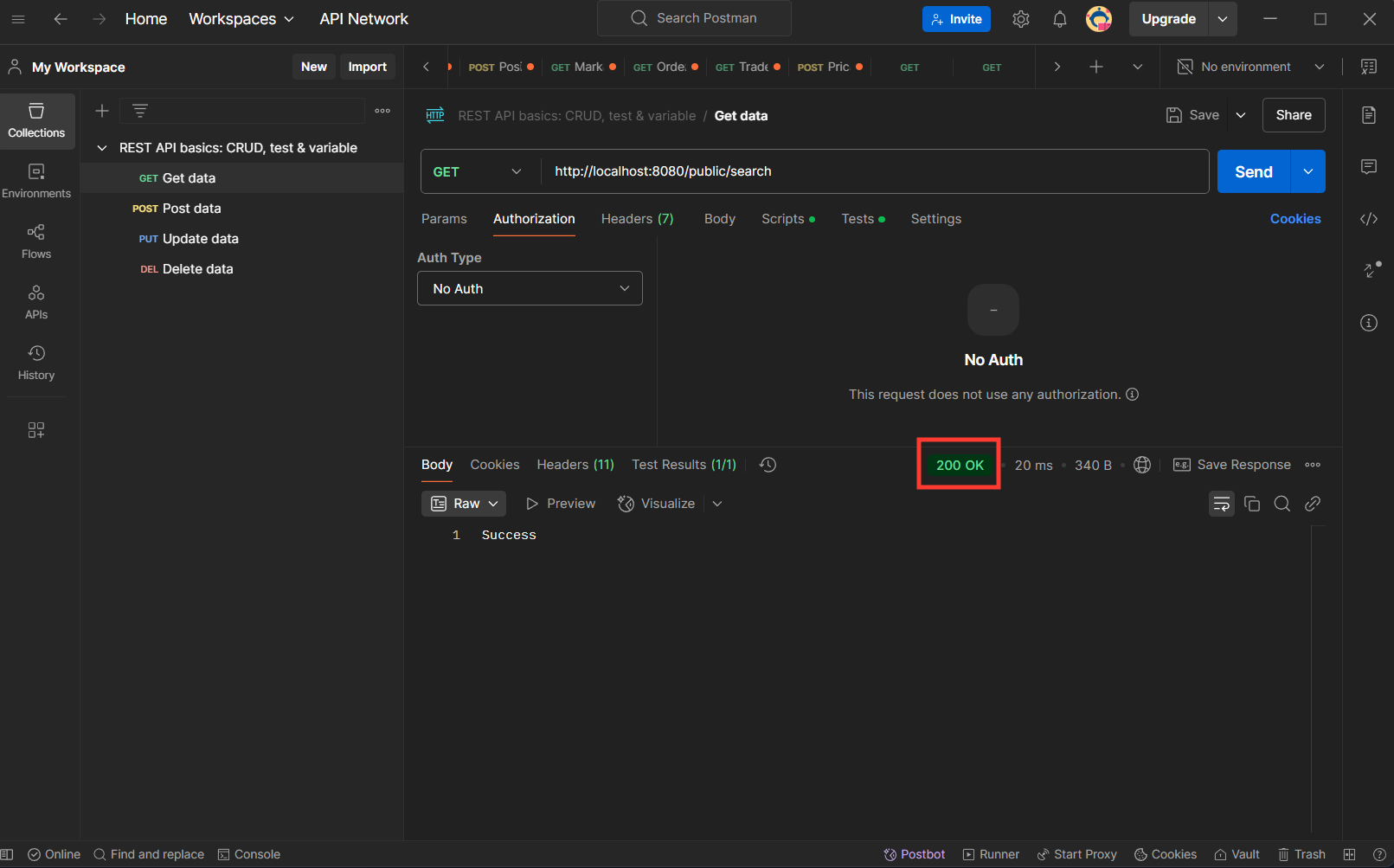
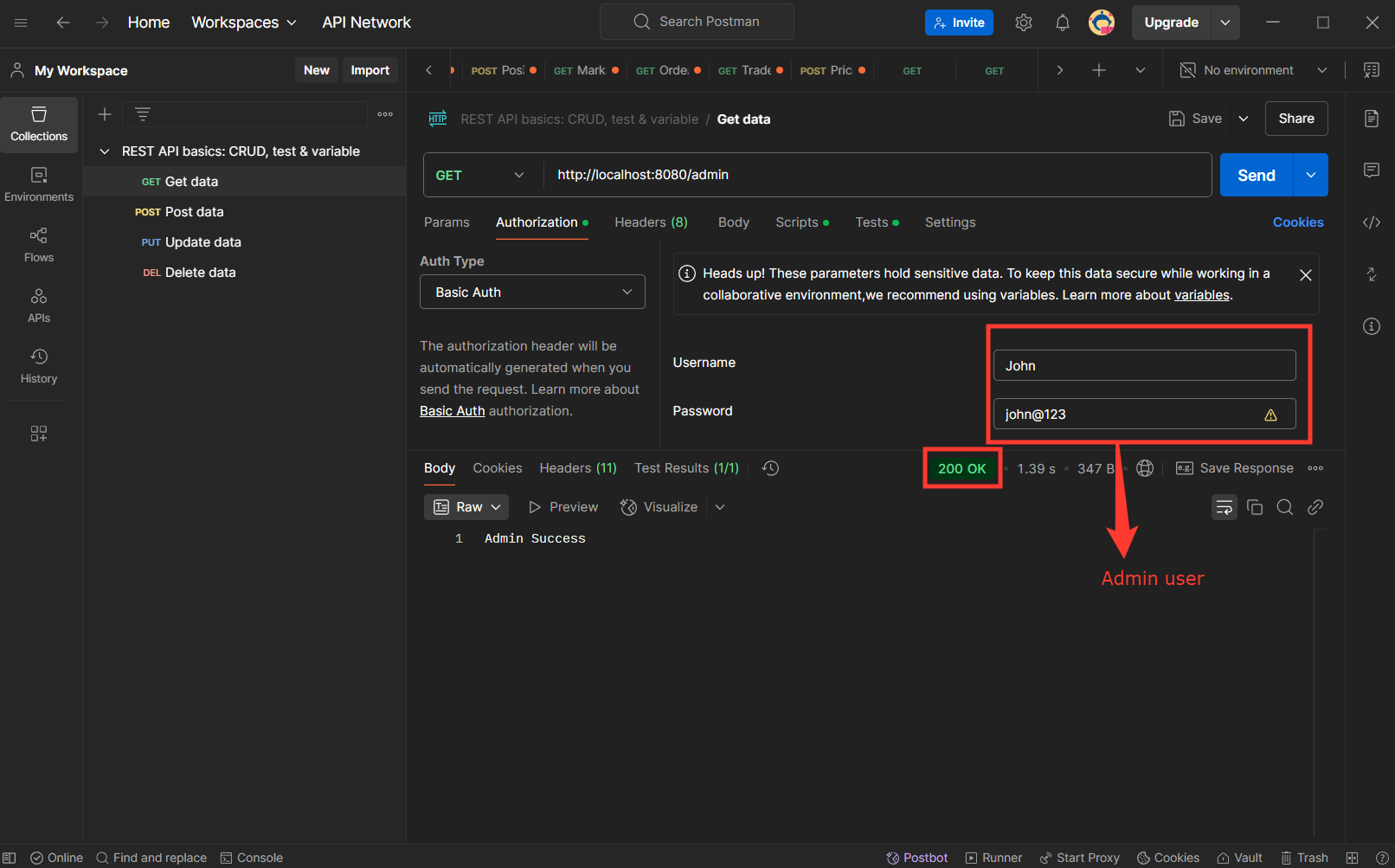
Testing the REST API with Postman:
Once the application is running, test the endpoints:
Get Public Route for all GET:http://localhost:8080/public/search
Get Admin user route GET:http://localhost:8080/admin
Get Admin and user route GET:http://localhost:8080/user