Advertisement
Google Ad Slot: content-top
Spring Boot One-to-Many and Many-to-One Mapping
- A One-to-Many relationship means one entity is related to multiple entities.
- A Many-to-One relationship means multiple child entities are related to a single parent entity.
Example:
✅ A User can have multiple Posts
✅ A Post belongs to only one User
Define User and Post Entities
We'll create a bidirectional One-to-Many relationship between User and Post.
✅ @OneToMany(mappedBy = "user") → Specifies that User is the parent.
✅ cascade = CascadeType.ALL → Ensures changes in User reflect in Post.
✅ orphanRemoval = true → Automatically deletes orphaned Post entries when removed from User.
✅ @JsonManagedReference → This marks the owning side (parent).
✅ @ManyToOne → Defines that Post belongs to a User.
✅ @JoinColumn(name = "user_id") → Creates a foreign key user_id in the Post table.
✅ @JsonBackReference → This marks the child side, preventing it from serializing the User field.
Table name : user
| id | name |
|---|
Table name : post
| id | title | user_id |
|---|
Create JPA Repositories
Create Services
Create Controllers
Testing the REST API with Postman for one-to-many:
Once the application is running, test the endpoints:
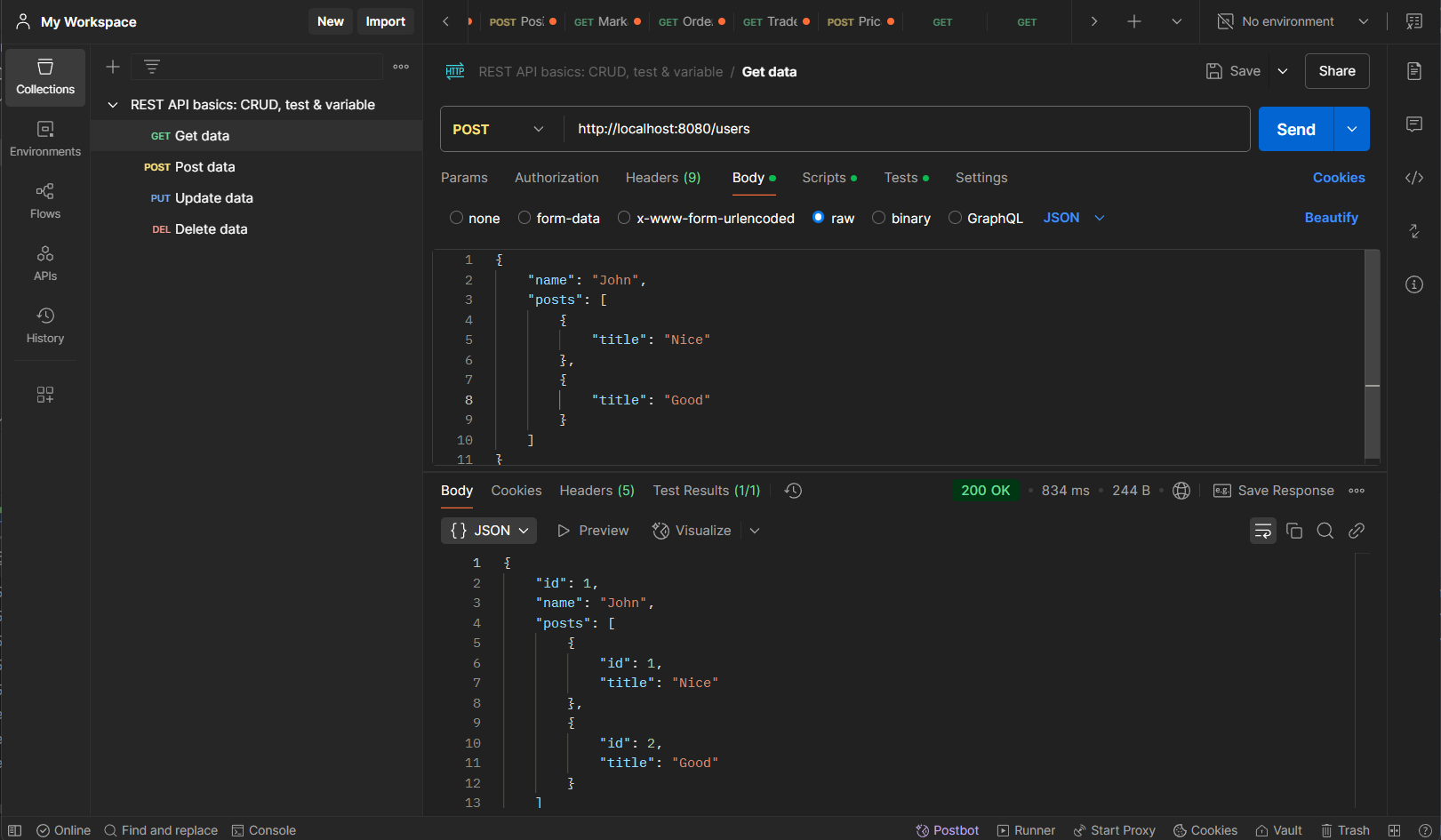
Create User http://localhost:8080/users
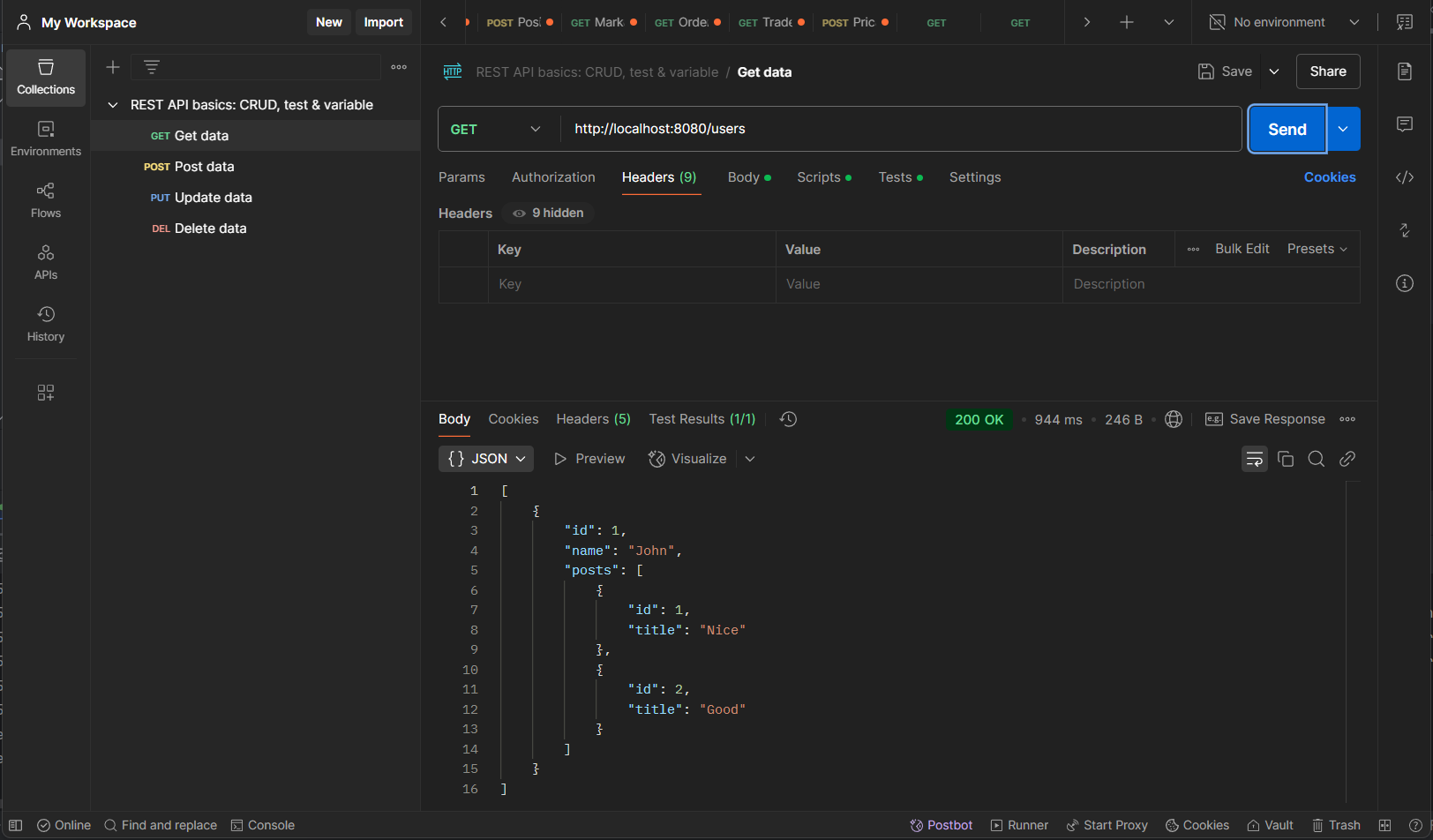
Get All Users http://localhost:8080/users
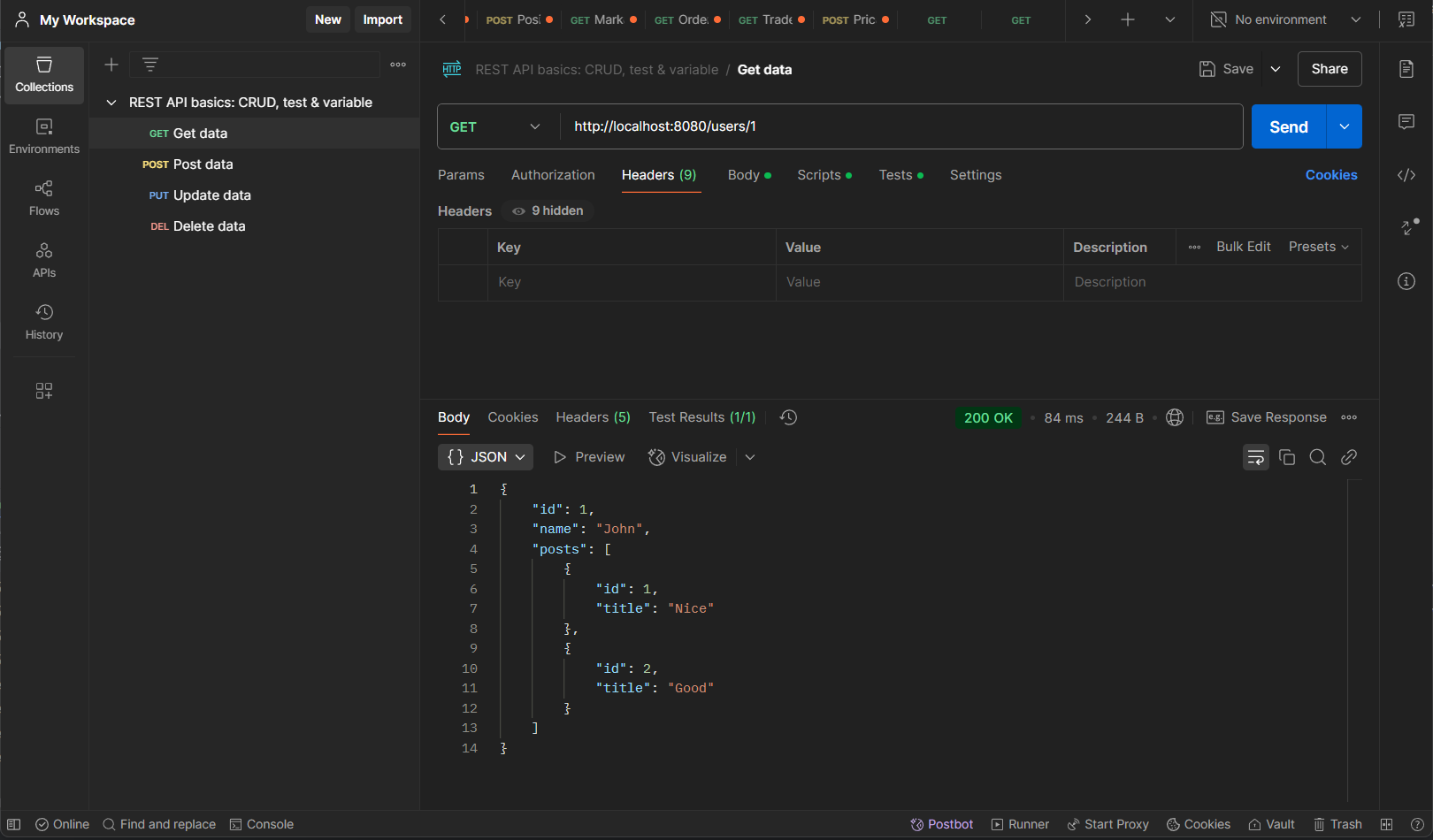
Get User By Id http://localhost:8080/users/{userID}
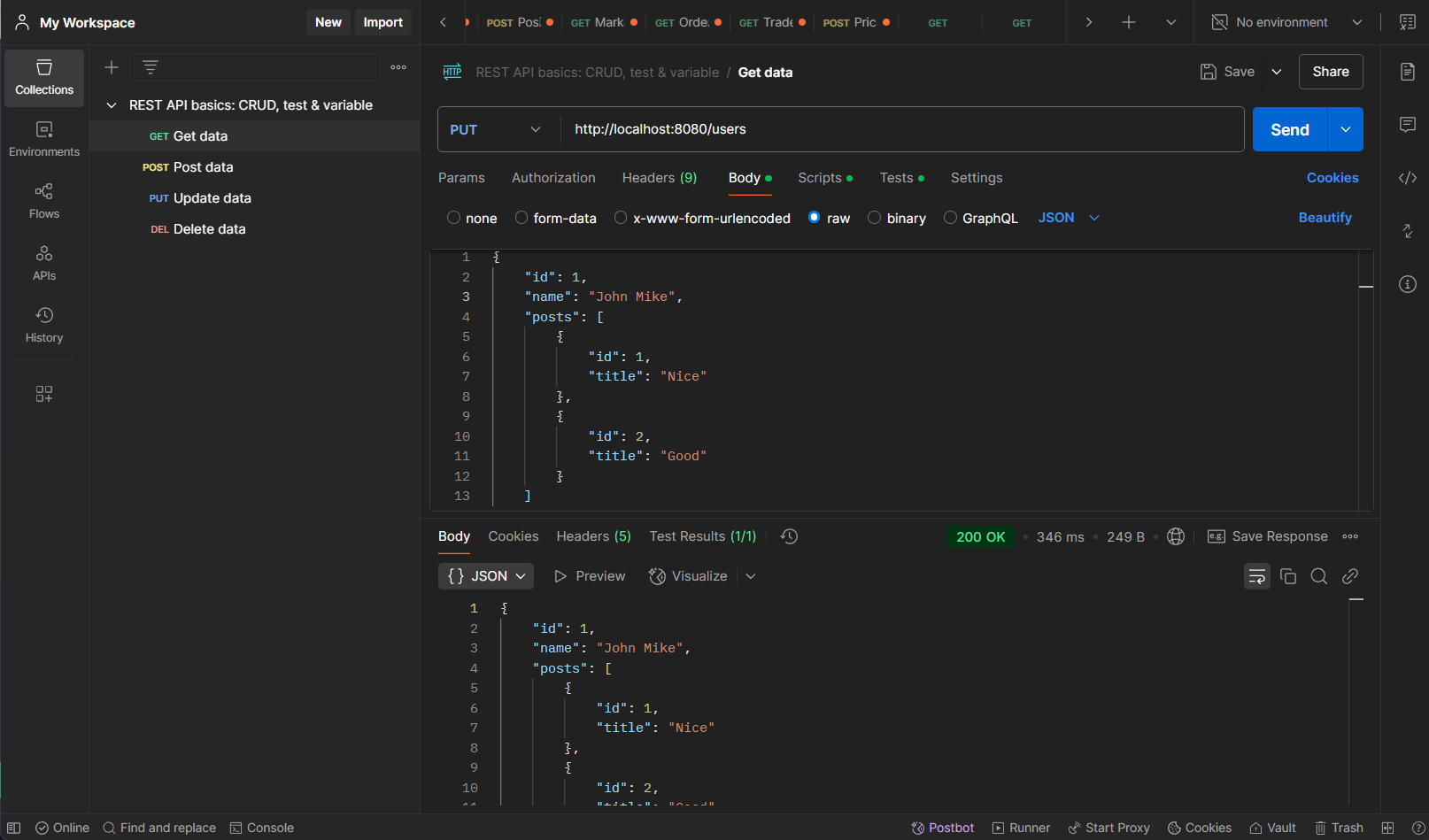
Update User http://localhost:8080/users
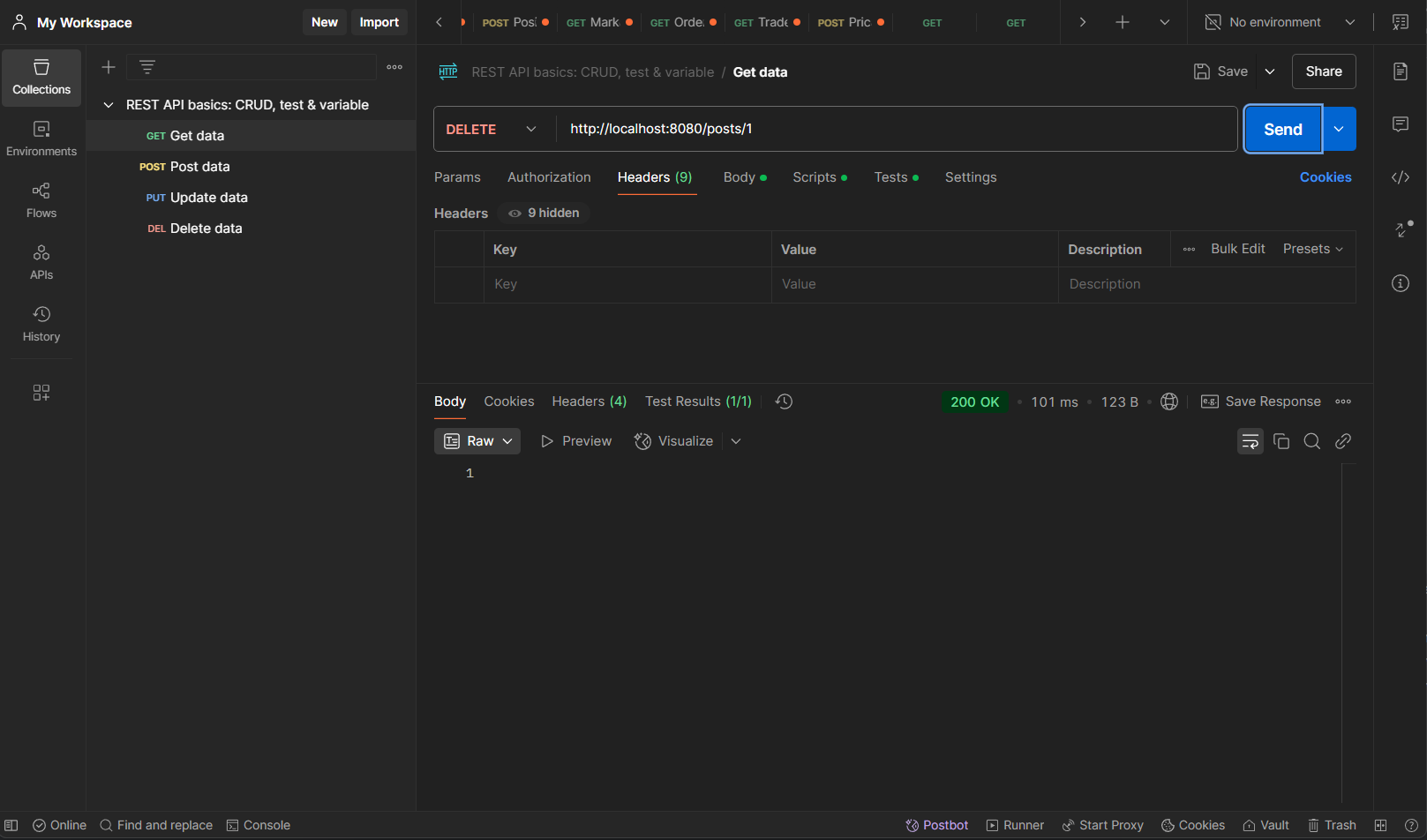
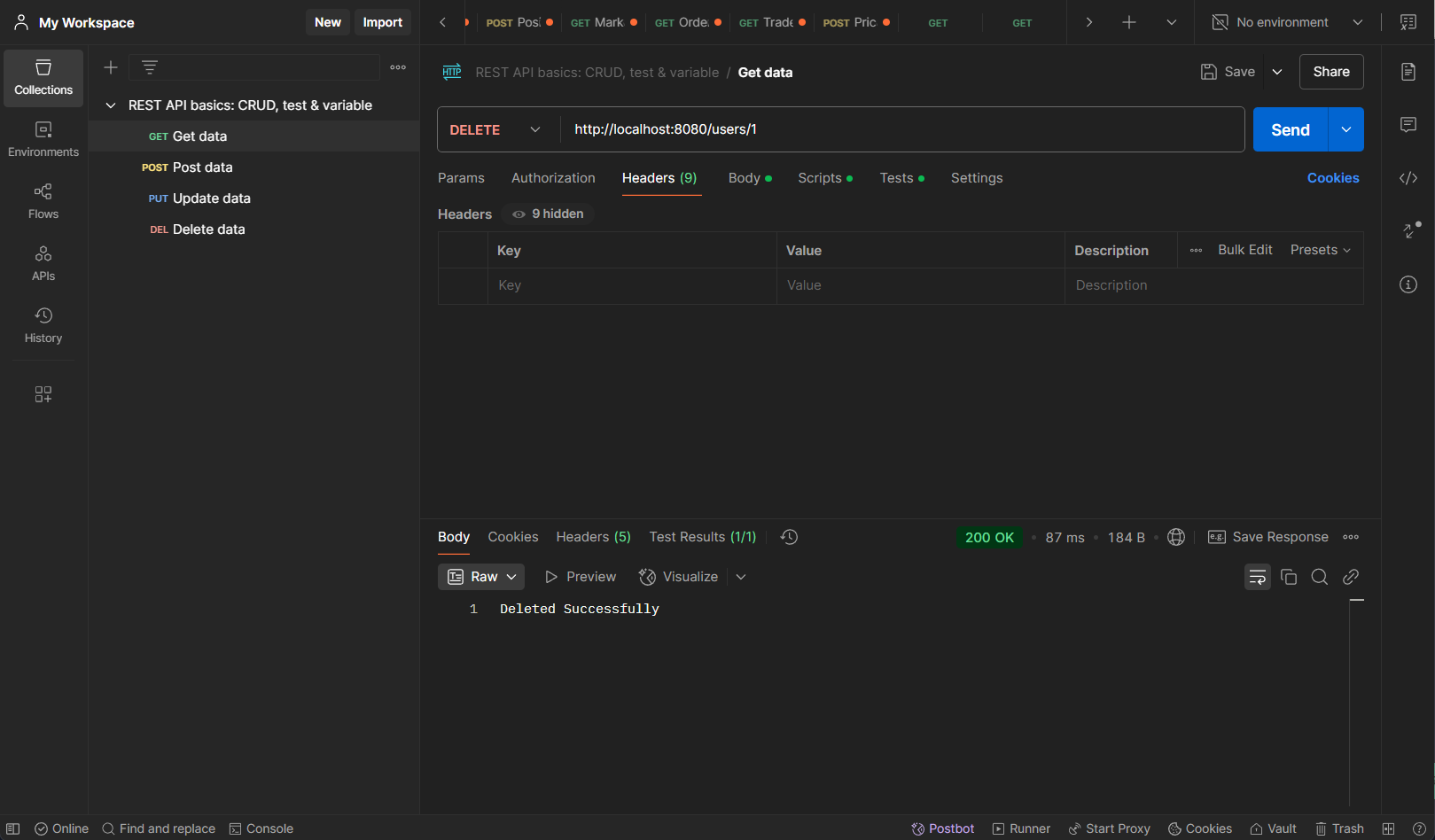
Delete User http://localhost:8080/users/{userID}
Testing the REST API with Postman for many-to-one:
Once the application is running, test the endpoints:
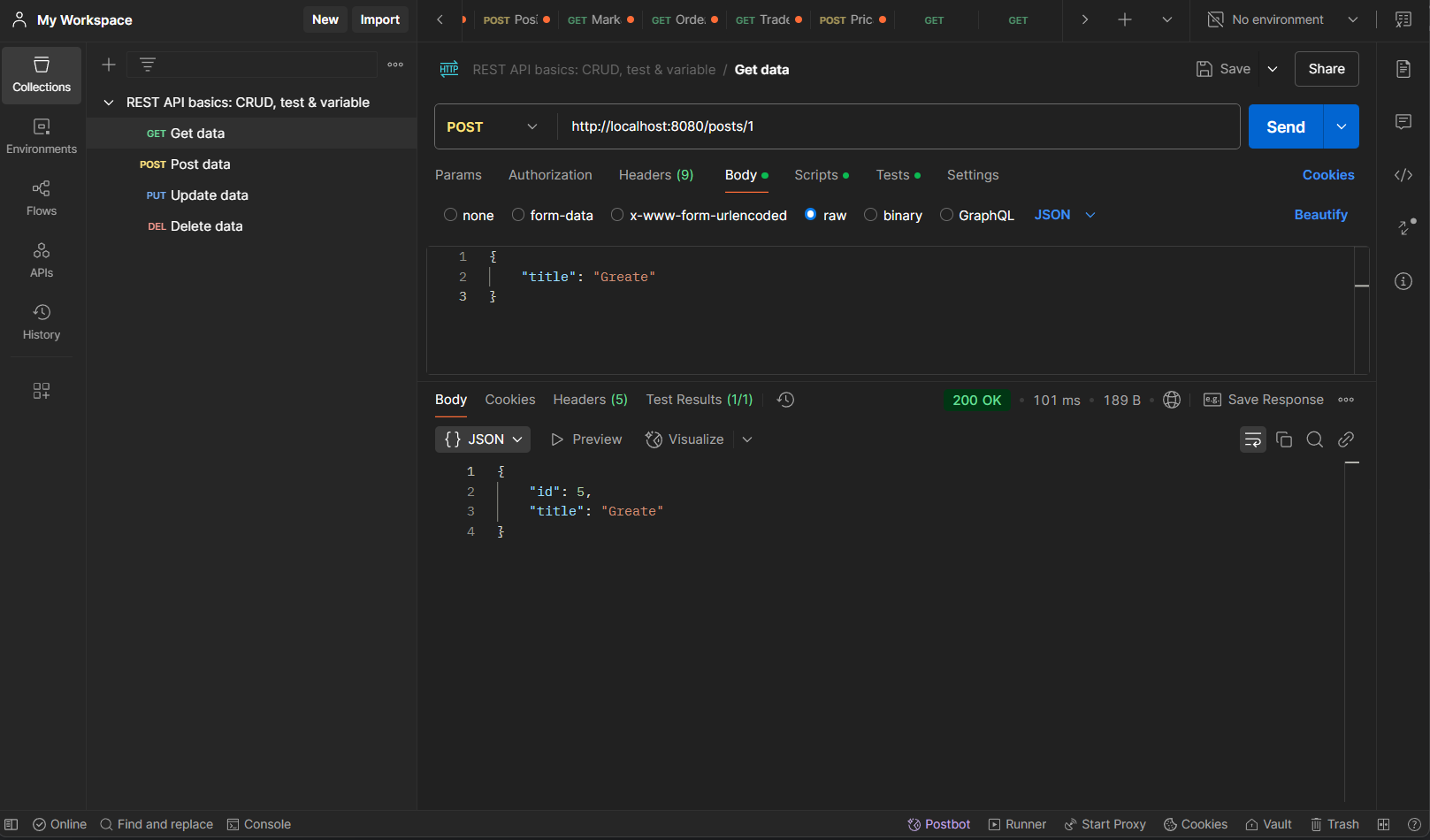
Create Post http://localhost:8080/posts/{userID}
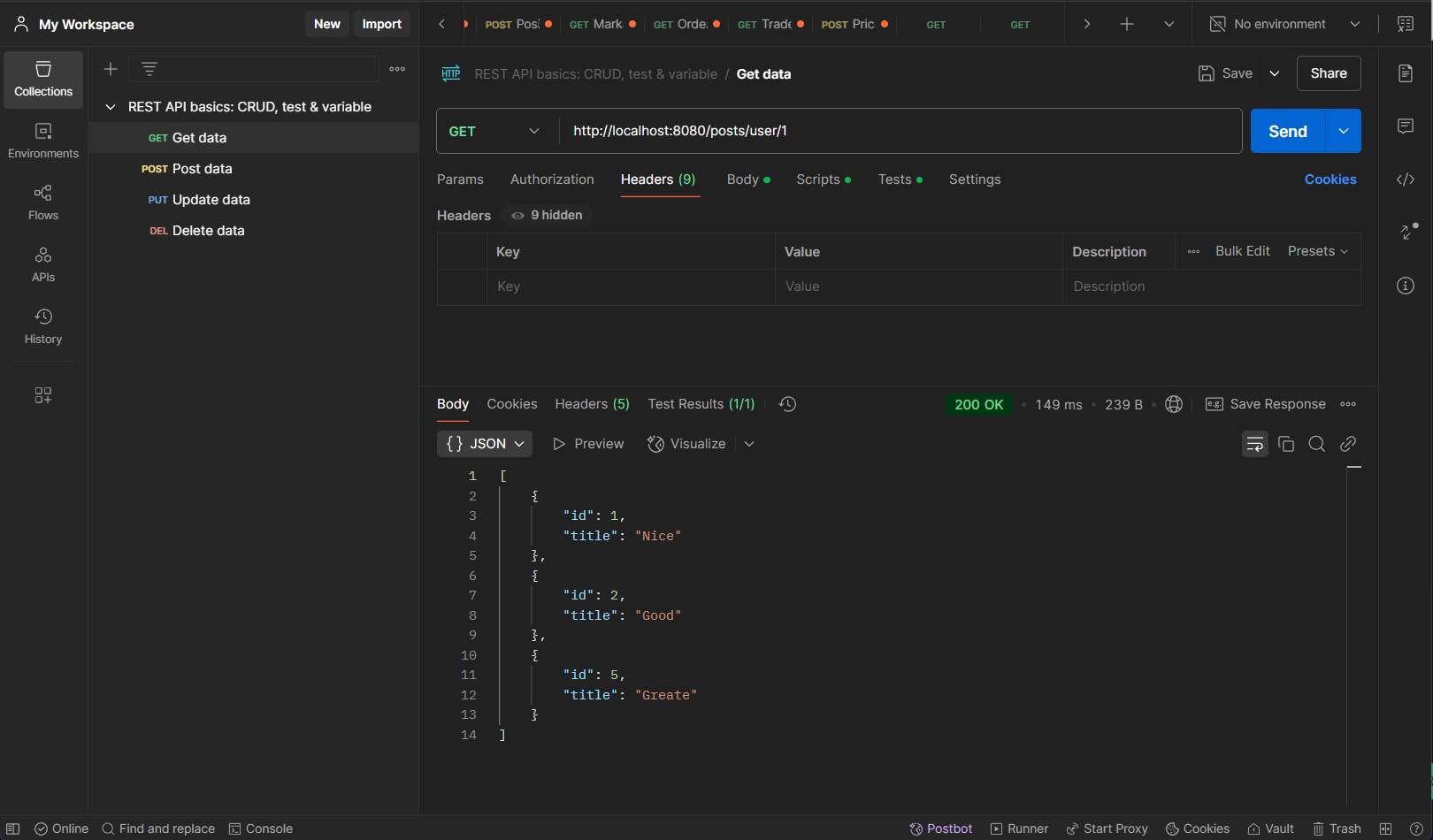
Get Posts by user id http://localhost:8080/posts/{userID}
Delete Posts http://localhost:8080/posts/{postID}