Advertisement
Google Ad Slot: content-top
Hibernate One-to-One Mapping
A one-to-one (1:1) relationship means that one entity is associated with exactly one other entity.
For example:
- One User has one Profile.
- One Employee has one Address.
Ways to Implement One-to-One Mapping:
Approach |
Description |
|---|---|
Using |
Uses a foreign key in one table. |
Using |
Uses a bidirectional relationship. |
Using |
Uses shared primary keys. |
One-to-One with @JoinColumn:
One User has One Profile
- User Table → Stores
id,name, and a reference toprofile_id. - Profile Table → Stores
idandbio.
Output
Table name : profiles
| id | bio |
|---|---|
| 1 | Java Developer |
Table name : users
| id | name | profile_id |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | John Doe | 1 |
One-to-One with mappedBy (Bidirectional):
- The
Profileentity owns the relationship (foreign key is inUser). mappedBy="profile"tells Hibernate thatProfileis responsible.
Output
Table name : users
| id | name |
|---|---|
| 1 | John Doe |
Table name : profiles
| id | bio | user_id |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Java Developer | 1 |
One-to-One with @PrimaryKeyJoinColumn (Shared Primary Key):
- Both
UserandProfileshare the same primary key.
Output
Table name : users
| id | name |
|---|---|
| 1 | John Doe |
Table name : profiles
| id | bio |
|---|---|
| 1 | Java Developer |
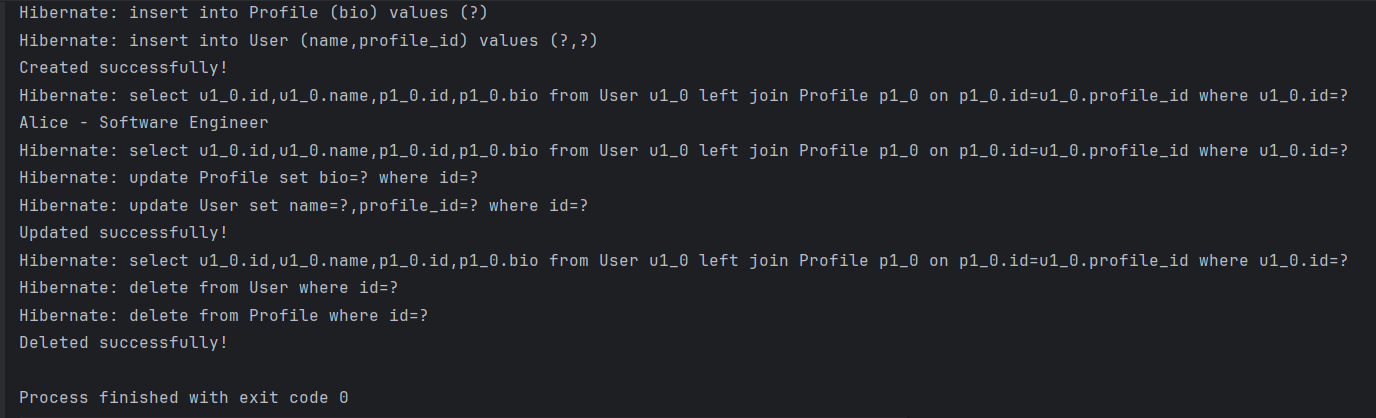
Create Read Update Delete (CRUD):
In this guide, we will implement CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations for a One-to-One Mapping using Hibernate.
Output